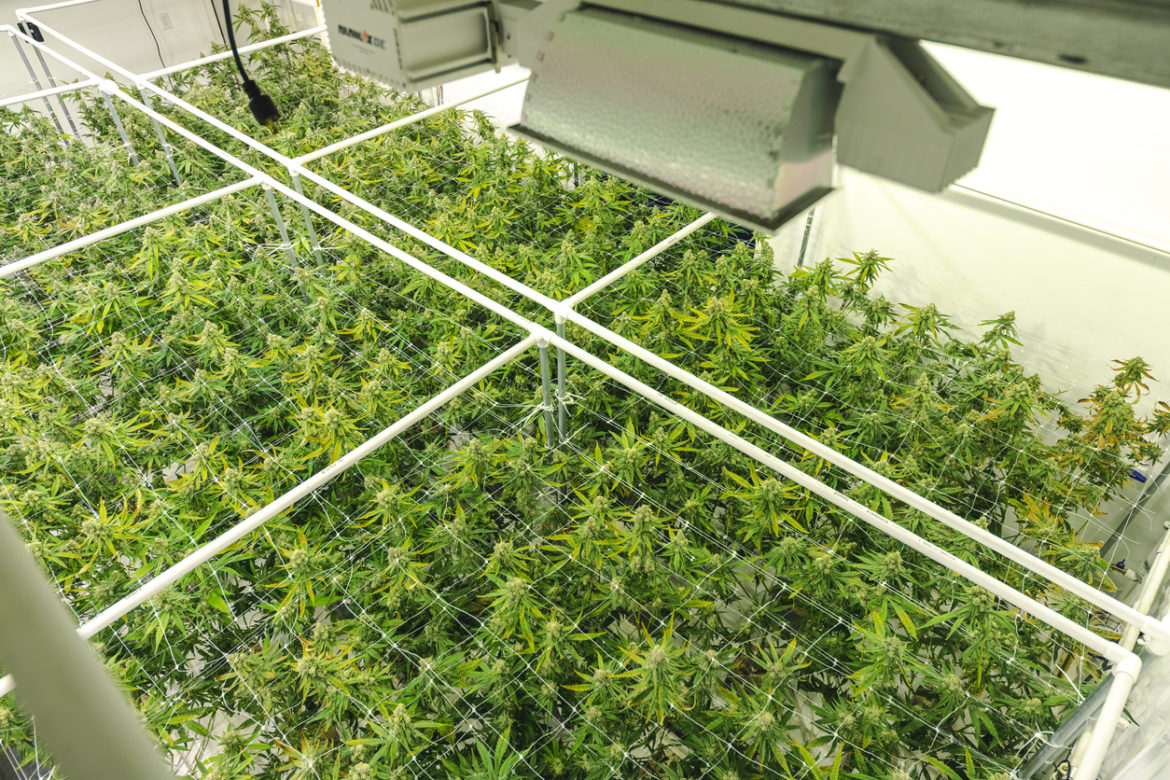

Cannabis Cultivation: Monitoring Nutrients in Plants
A bountiful harvest of the best cannabis is only achieved when the entire cultivation process pays careful attention to quality. As a grower, you are responsible for recognizing, diagnosing, and treating any issues that would threaten the health of your cannabis crop. There are several components to manage for a high-quality yield, and you must learn to balance the complex elements that work together for a healthy plant. Failing to follow proper cannabis cultivation techniques could result in crop failure or poor product integrity, two serious liability risks of legal cannabis cultivation.
Testing for pH
A slightly acidic environment is best for encouraging cannabis roots to thrive. With pH at the root, the plant can access the nutrients needed to grow. Levels that are too high or too low prohibit the plant from fully absorbing the nutrients required, leading to damaging deficiencies and leaf problems. An optimum root zone for pH is between 6.0 and 7.0. Check your root substrates with a digital pH pen or measurement kit with strips or drops. Check every two weeks and chart the results for proper cannabis cultivation.
Adding Nutrients for Best Quality
There are several nutrients to carefully watch when growing your crop. The macronutrients, or the ones needed in large quantities, are phosphorus, nitrogen, and potassium. These form the foundation of your plant’s health. Fertilizers use an NPK ratio to show the concentration of each nutrient in the compound. Secondary nutrients include:
- Calcium (creates cell wall development, encourages water penetration, reduces soil salinity)
- Magnesium (aids in photosynthesis, propels carbohydrate metabolism, and stabilizes cell walls)
- Sulfur (promotes the formation of chlorophyll, produces proteins, amino acids, and vitamins, and protects against disease)
Healthy cannabis cultivation also requires boron, copper, chlorine, iron, zinc, molybdenum, and manganese. While needed in much smaller quantities, micronutrients play an essential part in your crop’s health.
Feeding Your Crop
The different stages of cannabis cultivation and growth require different nutrients. Seedlings don’t need to be fed until they have developed 3-4 true leaves. As they enter the vegetative growth phase, use a lower NPK ratio fertilizer to avoid nutrient burn. By six weeks, you may begin a more aggressive nutrient supplement strategy, using a 10:5:7 NPK nutrient blend. As your crop beings to flower, you will slightly alter your ratio to feed more potassium and less nitrogen. Transitions to harvesting begin the start of a milder 4:7:10 NPK ratio.
Failing to Pay Attention
Underfeeding or overfeeding can cause stress in cannabis plants. Nutrient burns lead to dark green leaves with neon green tips. Plants may also have deep red or purple stems and branches. Deficiencies are seen in yellowing foliage, irregular leaf shapes, and brown spots. Overfeeding can cause dry, burnt leaves, brown or yellow discoloration, and upward bent tips. Without careful attention and monitoring, you can find yourself in danger of losing a healthy, high-quality crop.
About CannGen Insurance Services
For more information about our comprehensive insurance solutions for the cannabis, CBD, and hemp industries, please visit our website at www.canngenins.com or email marketing@canngenins.com.


 US
US
 US
US
 CA
CA
 EU
EU
